
1. Matplotlib 데이터 시각화
▶ Matplotlib 라이브러리
: 저수준의 그래픽용 라이브러리
▶ 참고 사이트
https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.subplots.html
matplotlib.pyplot.subplots — Matplotlib 3.7.1 documentation
ax can be either a single Axes object, or an array of Axes objects if more than one subplot was created. The dimensions of the resulting array can be controlled with the squeeze keyword, see above. Typical idioms for handling the return value are: # using
matplotlib.org
01. Matplotlib 기본 사용
 Matplotlib 라이브러리를 이용해서 그래프를 그리는 일반적인 방…
wikidocs.net
▶ 라이브러리 설치 및 가져오기
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
matplotlib.__version__
2. 라인그래프 / 관련 옵션 사용자화
▶ plot()
: 라인 그래프 생성 함수
: 숫자 데이터를 입력해서 간단한 라인그래프 출력 후 여러 옵션 설정
▶ 시각화 할 데이터 입력 방법
: plot() 함수에 직접 입력 (그래프)
: 넘파이_array 형태로 입력
: 데이터프레임_열(컬럼) 입력
2-1) plot() 함수에 데이터를 직접 입력
plt.plot([2, 1, 5, 3, 7, 8, 13])
plt.show()
2-2) 넘파이_배열 데이터로 입력
data = np.arange(10)
dataplt.plot(data)
plt.show()
2-3) x, y 데이터 직접 입력
data_x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
data_y = [2, 3, 5, 10]
plt.plot(data_x, data_y)
plt.show()
2-4) 데이터프레임의 열(컬럼)을 입력하여 그래프 출력하기
▶ seaborn 라이브러리 설치 및 'iris' 데이터셋 불러오기
import seaborn as sns
iris = sns.load_dataset('iris')
▶ iris 데이터 중 sepal_length 열의 데이터 시각화
plt.plot(iris.sepal_length)
plt.show()
3. 옵션 사용자화
3-1) x축, y축 레이블 설정하기
: labelpad = 그래프와 레이블 사이의 여백 설정
: fontdict = 폰트 타입과 스타일 관련 설정
-폰트 두께('fontweight') : 'normal' , 'bold', 'heavy’, ‘light’, ‘ultrabold’, ‘ultralight’
-폰트 타입('family') : 'arial'
- 폰트 사이즈 : 숫자로 입력
data_x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
data_y = [1, 7, 5, 12]
plt.plot(data_x, data_y)
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label', labelpad = 12, fontdict = {'color' : 'hotpink', 'size' : 14})
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label', labelpad = 12, fontdict = {'color' : 'red', 'size' : 14})
plt.show()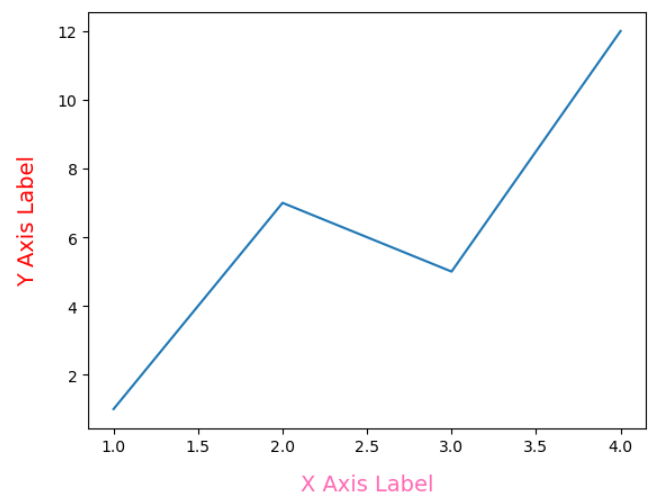
3-2) 범례 표시하기
: legend() 함수 → 데이터의 범례 표시
: 그래프가 1개인 경우와 2개 이상인 경우
▶ legend(loc = )
: 매개변수 loc을 활용하여 위치를 지정
: legend(loc = (0.0, 0.0)) 의 위치는 하단 왼쪽 끝점
: legend(loc = (1.0, 1.0)) 의 위치는 상단 오른쪽 끝점
◆ loc 입력 가능 옵션
: best, upper right, upper left, lower left, lower right, right, center left, center right, lower center, upper center, center
* 1개 데이터 그래프 범례 표시
: 데이터 1개를 플로팅하는 경우 범례를 사용하면 기본적으로 왼쪽 상단에 생성됨
plt.plot(data_x, data_y, label = 'Data ABC')
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.legend(loc = (0.05, 0.9))
plt.show()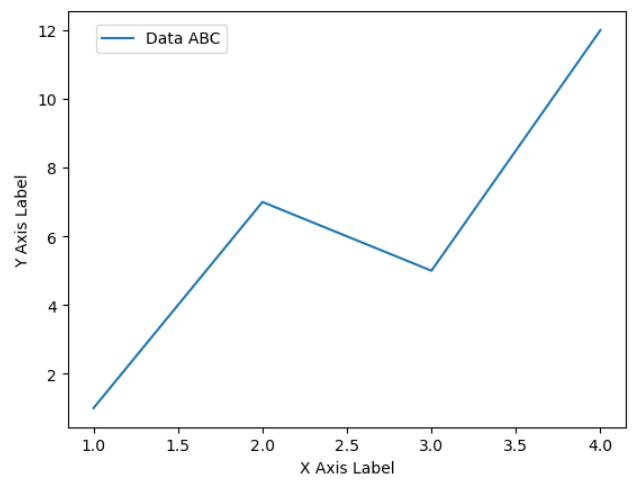
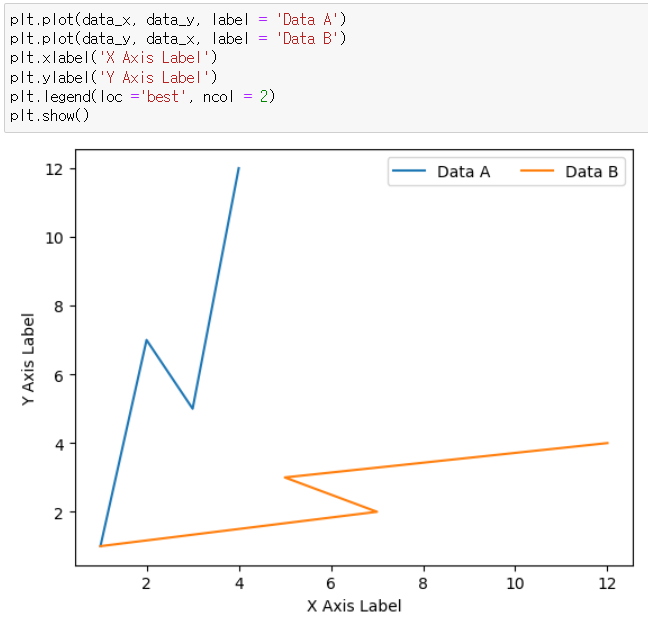
* 2개 데이터 그래프 범례 표시
▶ legend(loc = 'best, ncol = )
: 'best' 입력하면 자동으로 적당한 위치에 표시
: ncol = 로 2개의 데이터를 시각화 할 때 범례 설정
plt.plot(data_x, data_y, label = 'Data A')
plt.plot(data_y, data_x, label = 'Data B')
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.legend(loc ='best', ncol = 2)
plt.show()
* ncol = 2 인 경우 범례를 2개의 열로 생성
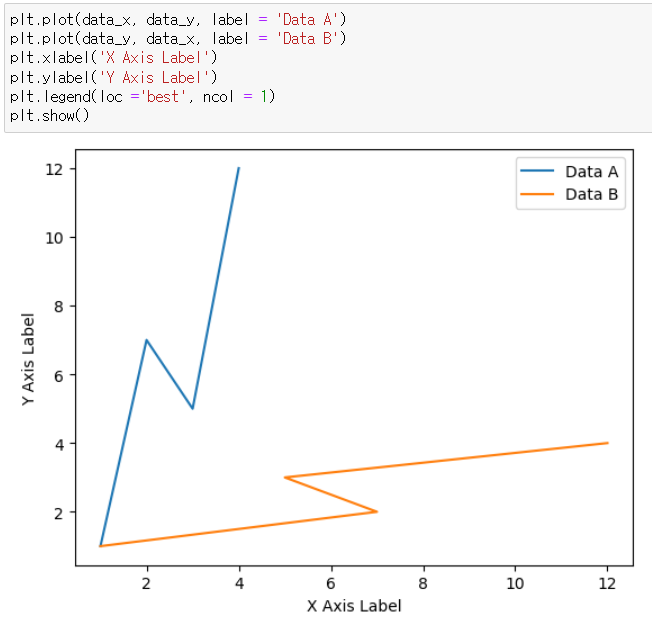
* ncol = 1 인 경우 범례를 1개의 열로 생성
3-3) x축, y축 범위 정하기
: 기본적으로 축의 범위는 데이터의 최솟값/최댓값을 기준으로 설정
: xlim(), ylim() 함수로 축의 범위 자유롭게 조정 가능
▶ xlim / ylim( [축 최솟값, 축 최댓값] )
plt.plot(data_x, data_y)
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.xlim([0, 6])
plt.ylim([0, 15])
plt.show()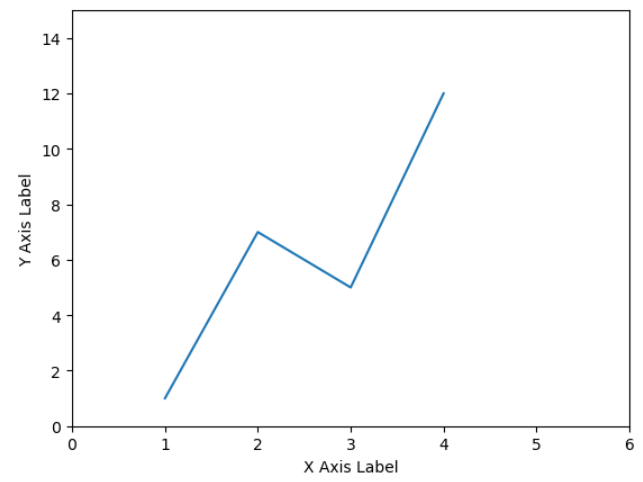
▶ axis(x 최솟값, x축 최댓값, y축 최솟값, y축 최댓값)
plt.plot(data_x, data_y)
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.axis([0, 6, 0, 15])
plt.show()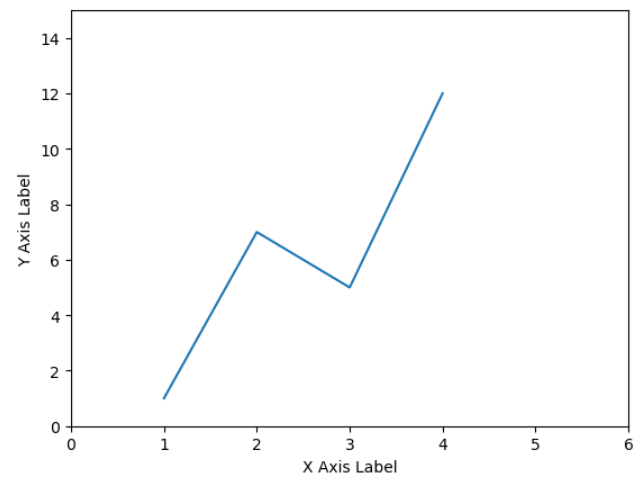
3-4) 색깔 지정하기
: 그래프에 색깔을 지정하지 않으면 기본적으로 Matplotlib 기본 팔레트 10개 색상 순서대로 출력
: plot() 함수의 매개변수 color로 컬럼을 지정 가능, 특정 컬러를 표현하는 문자로도 입력 가능
◆ Matplotlib 라이브러리에 명명된 색상 이름 사용하기
: 그래프를 초록색으로 표현하고 싶은 경우 color에 'green' 이라고 입력해도 되나, 'g'라고 입력해도 됨
: 검은색도 'black' 또는 'k'로 입력할 수 있음
plt.plot(data_x, data_y, color = 'g')
plt.show()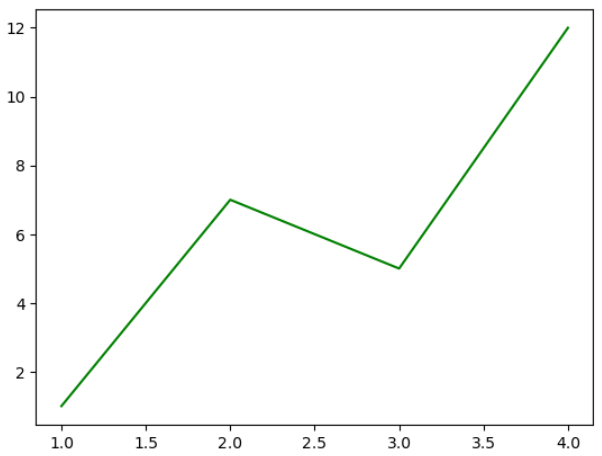
▶ hex 코드 사용하기
: RGB 색상 코드 표기법
: #ff0000 형식의 컬러 코드. #과 뒤에 붙는 여섯 자리 또는 세자리 숫자로 표기하는 방식
: 원하는 hex 코드를 찾아서 입력할 수 있음
◆ hex 코드를 제공
htmlcolorcodes.com

3-5) 선 스타일 지정하기
: 라인 그래프를 출력하면 기본적으로 솔리드 타입으로 그려짐
: plot() 함수의 매개변수 linestyle로 지정 가능
▶ 선 스타일 4가지( sold, dashed, dotted, dashdot )
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 1, 3, 5], linestyle='solid', color='g', label='solid')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 2, 4, 6], linestyle='dashed', color='g', label='dashed')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 5, 7], linestyle='dotted', color='g', label='dotted')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 4, 6, 8], linestyle='dashdot', color='g', label='dashdot')
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.axis([0.5, 4.5, 0, 9])
plt.show()
▶ 선 스타일_capstyle =
: butt 각진 것
: round 둥근 것
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 1, 3, 5], linestyle='solid', solid_capstyle='butt', color='g', linewidth=8, label='solid')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 2, 4, 6], linestyle='solid', solid_capstyle='round', color='g', linewidth=8, label='dashed')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 5, 7], linestyle='dashed', dash_capstyle='butt', color='lightgreen', linewidth=8, label='dotted')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 4, 6, 8], linestyle='dashed', dash_capstyle='round', color='lightgreen',linewidth=8, label='dashdot')
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.axis([0.5, 4.5, 0, 9])
plt.show()
▶ marker 스타일
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 1, 3, 5], marker='o', color='g', label='data A marker')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 5, 7], marker='s', color='limegreen', label='data B marker')
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.axis([0.5, 4.5, 0, 8])
plt.show()
▶ o-- / x:
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 1, 3, 5], 'o--', color='g', label='solid + marker')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 5, 7], 'x:', color='limegreen', label='dashed + marker')
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.axis([0.5, 4.5, 0, 8])
plt.show()
3-6) 그리드 표시하기
: plot() 함수에 grid() 함수를 결합하면 그리드를 표시할 수 있음
: 그리드를 표시하면 데이터를 정확하게 파악 할 수 있는 장점이 있음
▶ grid(True)
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 1, 3, 5], linestyle = 'solid', color = 'g', label = 'solid')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 5, 7], 'x:', color = 'limegreen', label = 'dashed + marker')
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.legend(loc = 'best')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
▶ grid(True, 매개변수 = )
: alpha = 는 투명도를 의미함
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 1, 3, 5], linestyle = 'solid', color = 'g', label = 'solid')
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 5, 7], 'x:', color = 'limegreen', label = 'dashed + marker')
plt.xlabel('X Axis Label')
plt.ylabel('Y Axis Label')
plt.legend(loc = 'best')
plt.grid(True, axis = 'y', color = 'red', alpha = 0.9, linestyle = '-.')
plt.show()
3-7) 타이틀 설정하기
: title() 함수로 그래프 타이틀 설정
: loc = 으로 위치 설정
: pad = 로 그래프와 공백 지정
▶ 타이틀 설정
: font_style 이라는 변수에 폰트 설정을 담아두고,
: title 매개변수 fontdict에 font_style 입력
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 1, 3, 5], linestyle = 'solid', color = 'g', label = 'solid')
plt.legend(loc = 'best')
plt.grid(True, axis = 'y', alpha = 0.25)
font_style = {
'fontsize' : 25,
'fontweight' : 'heavy' # {‘normal’,‘bold’, 'heavy’,‘light’,‘ultrabold’,‘ultralight’} 설정 가능
}
plt.title('Title of Chart', fontdict = font_style, loc = 'center', pad = 15)
plt.show()
▶ subplot()
: 먼저 레이아웃을 몇 개 행 / 열로 나눌 것인지 기준 정하기
: subplot(행 수, 열 수, 인덱스 수)
* 행 2개, 열 1개, 인덱스 2개
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 1, 7], linestyle = 'solid', color = 'g', label = 'solid')
plt.xlabel('speed')
plt.ylabel('Data A')
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 2, 9, 6], linestyle = 'solid', color = 'red', label = 'solid')
plt.xlabel('speed')
plt.ylabel('Data B')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
* 행 1개, 열 2개, 인덱스 2개
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 1, 7], linestyle = 'solid', color = 'g', label = 'solid')
plt.xlabel('speed')
plt.ylabel('Data A')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 2, 9, 6], linestyle = 'solid', color = 'red', label = 'solid')
plt.xlabel('speed')
plt.ylabel('Data B')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()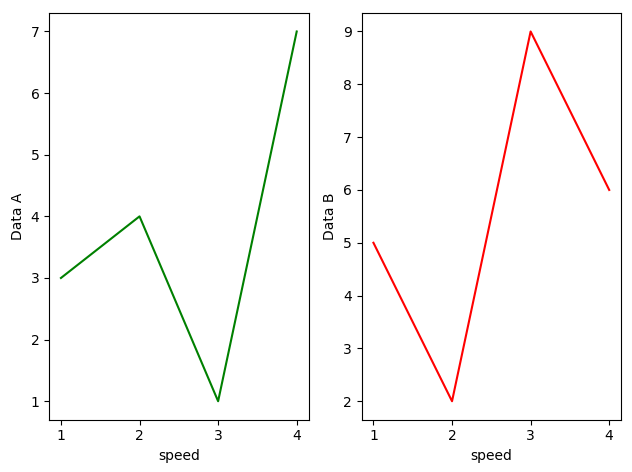
4. 히스토그램_데이터 분포 확인
▶ hist()
: 히스토그램 생성 함수
: 초반에 특정 변수의 분포를 시각화할 때 히스토그램을 사용
▶ iris 데이터셋 불러오기
iris = sns.load_dataset('iris')
iris.head()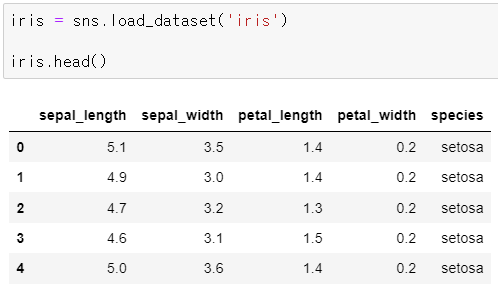
▶ 특정 행 시각화하기
plt.hist(iris.sepal_length, color = 'hotpink')
plt.show()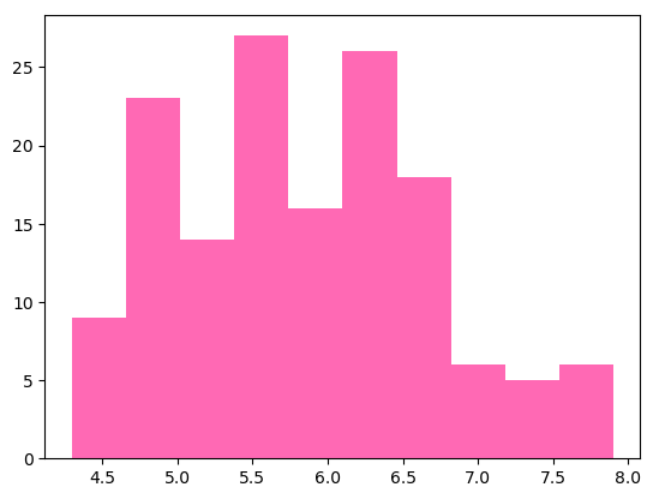
▶ 2개의 데이터 동시에 시각화하기
: 2개 이상의 변수를 동시에 시각화하는 경우 hist() 함수에 lable을 지정하지 않아도 출력 되지만 가독성을 위해 지정해주는 것이 좋음
plt.hist(iris.sepal_length, bins = 20, label = 'sepal_length', color = 'skyblue')
plt.hist(iris.petal_length, bins = 20, label = 'petal_length', color = 'violet')
plt.legend(loc = 'upper right')
plt.show()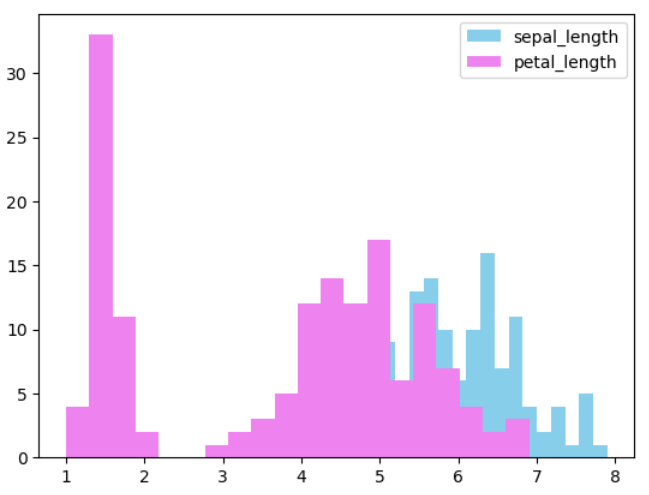
4-1) 누적 히스토그램 시각화
▶ 매개변수 cumulative = True / False
: True → 누적O
: False → 누적X
plt.hist(iris.sepal_length, cumulative = True, label = 'cumulative', color = 'skyblue')
plt.hist(iris.sepal_length, cumulative = False, label = 'not cumulative', color = 'violet')
plt.legend(loc = 'upper left')
plt.show()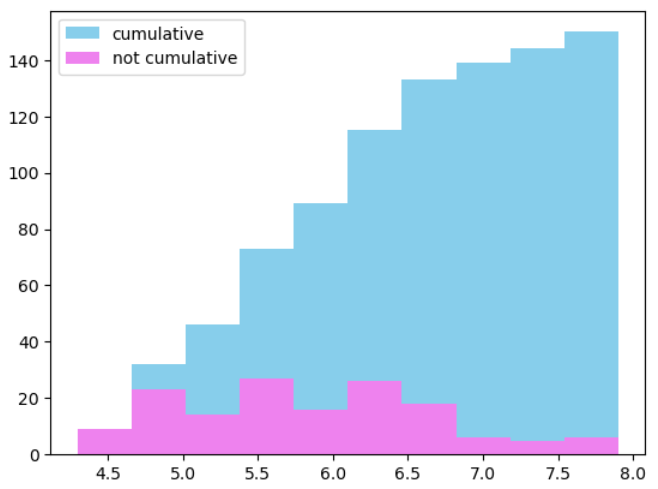
4-2) 히스토그램 4가지 타입
▶ 매개변수 histtype =
: bar, barstacked, step, stepfilled 타입이 있음
* subplot() 함수로 히스토그램의 4가지 타입 한 번에 출력해보기
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (10, 6))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 4)
ax1.hist((iris.sepal_length, iris.petal_length), histtype = 'bar')
ax2.hist((iris.sepal_length, iris.petal_length), histtype = 'barstacked')
ax3.hist((iris.sepal_length, iris.petal_length), histtype = 'step')
ax4.hist((iris.sepal_length, iris.petal_length), histtype = 'stepfilled')
ax1.title.set_text('Type : bar')
ax2.title.set_text('Type : barstacked')
ax3.title.set_text('Type : step')
ax4.title.set_text('Type : stepfilled')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()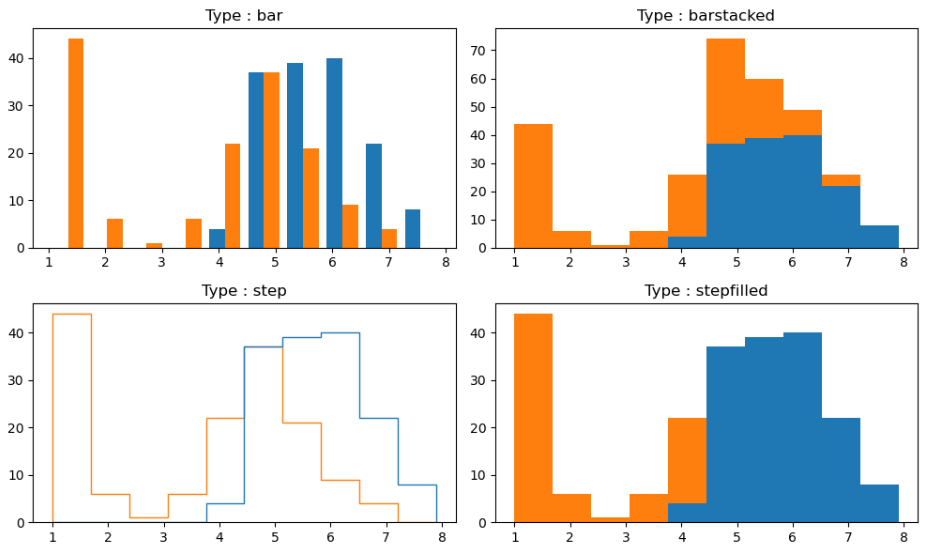
▶ species 별로 petal_length의 평균 구하기
* species 열의 데이터 확인
iris.species.unique()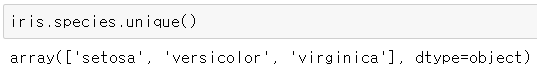
* petal_length 평균 구하기
iris_petal_length_mean = iris.groupby('species').petal_length.mean()
iris_petal_length_mean
5. 막대그래프_범주형 데이터 개수 확인
▶ bar()
: 막대그래프 생성 함수
: bar(x축 값, y축 값)
: 카테고리 타입의 데이터에 가장 많이 사용됨
▶ 데이터를 막대그래프로 시각화
* species 별로 petal_length의 평균 구하고 시각화
: x축 값에는 unique()를 사용해 고유한 species 값을 표시하고, y축 값에는 groupby()를 사용해 각 species 별 평균을 구함
plt.bar(iris.species.unique(), iris.groupby('species').petal_length.mean())
plt.show()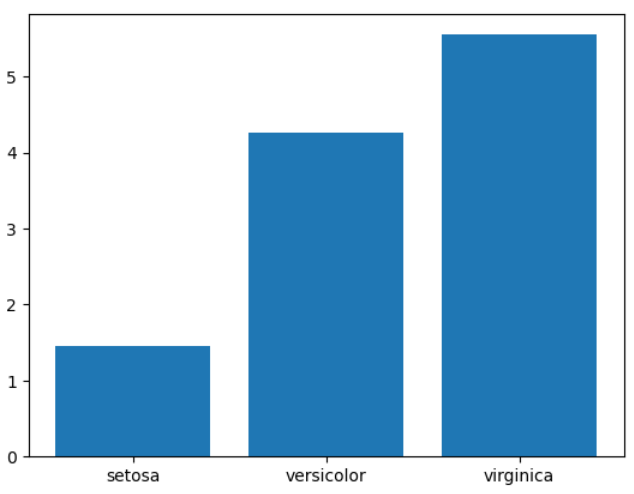
* 막대그래프 색깔 변경하기
plt.bar(iris.species.unique(), iris_petal_length_mean, color = 'mediumseagreen')
plt.show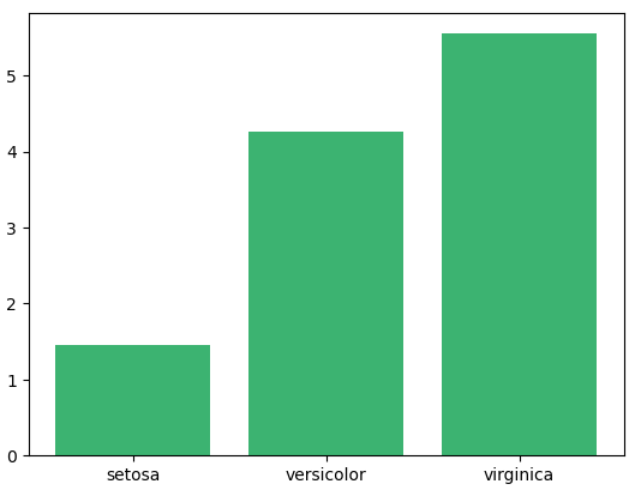
* 개별 막대마다 색깔 지정 + 막대 너비 지정
plt.bar(iris.species.unique(), iris_petal_length_mean, color = ['gold', 'mediumseagreen', 'teal'],
width = 0.5)
plt.show()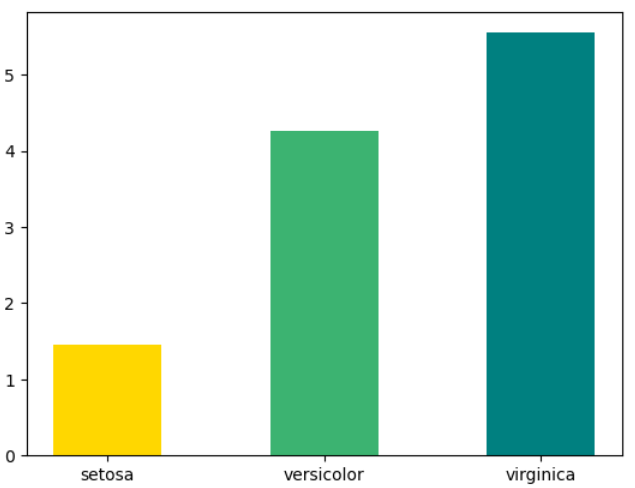
* 수평 형태의 막대그래프 그리기
: barh(x축 값, y축 값)
plt.barh(iris.species.unique(), iris_petal_length_mean)
plt.show()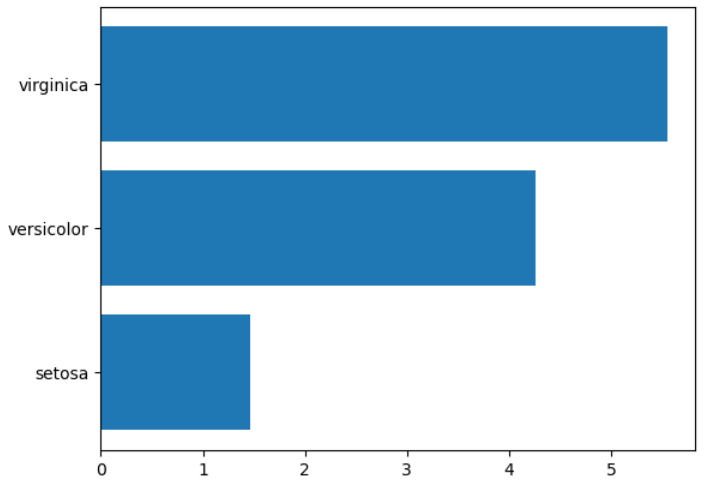
6. 산점도_수치형 데이터 상관관계
▶ scatter()
: 산점도 생성 함수
: scatter(x축 값, y축 값)
: 2개의 수치형 변수 간에 관계를 살펴볼 때 유용
: 두 변수 간의 관계가 선형인지 비선형인지 확인해 방향성과 강도 파악
: 이상값을 찾기에도 활용 가능
▶ 데이터를 산점도로 시각화
* petal_length와 petal_width 간 산점도 분포 확인하기
plt.scatter(x = iris.petal_length, y = iris.petal_width)
plt.show()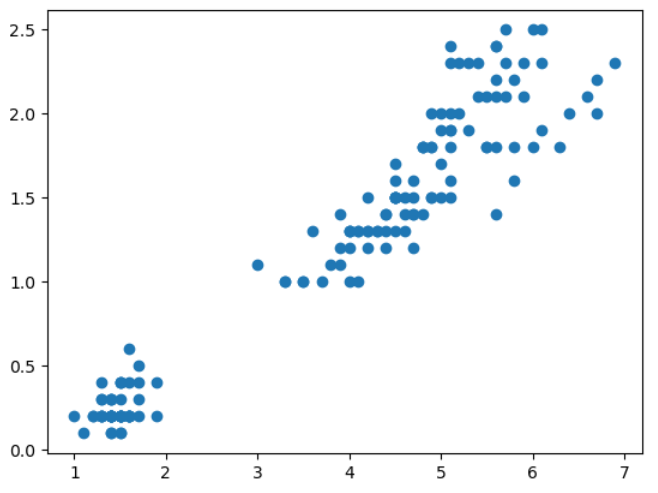
>> petal(꽃잎) length(길이)가 클수록 width(너비)도 커지는 것을 알 수 있음
7. 박스 플롯_데이터 분포 확인 및 이상값 찾기
▶ boxplot()
: 데이터의 분포를 사분위수 기준으로 표현
: 히스토그램처럼 데이터의 분포를 살펴 볼 때나 이상값을 찾을 때 사용
▶ 데이터를 박스플롯으로 시각화
plt.boxplot([iris.sepal_length, iris.sepal_width, iris.petal_length, iris.petal_width])
plt.show()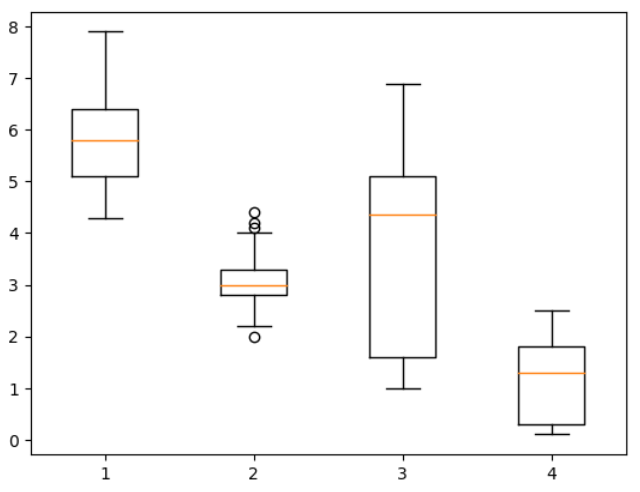
>> 원으로 표시된 부분이 이상값
* 이상값 조정하기
: 매개변수 whis = 값 조정
: whis의 기본값은 1.5
plt.boxplot([iris.sepal_length, iris.sepal_width, iris.petal_length, iris.petal_width],
notch = True, whis = 2.0): whis = 2.0으로 늘려주면 이상값의 개수가 줄어듦
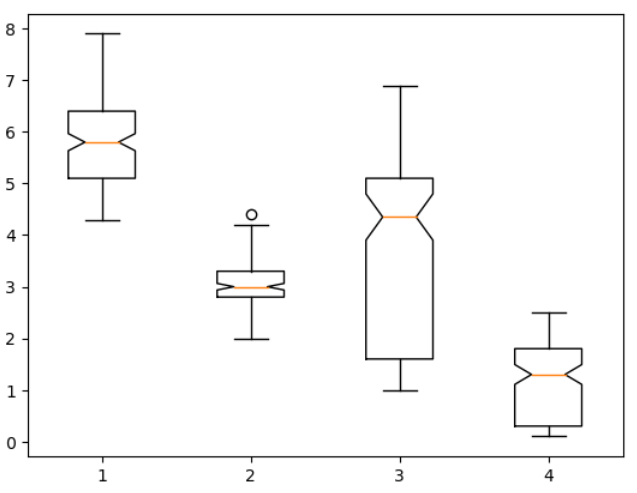
* 수평 형태의 박스플롯 그리기
: vert = False
plt.boxplot([iris.sepal_length, iris.sepal_width, iris.petal_length, iris.petal_width], vert = False)
plt.show()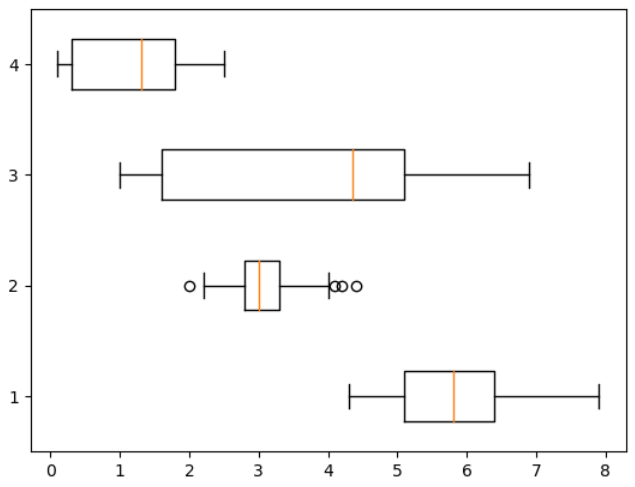




댓글